New York Times got the Hong Kong fire completely wrong


A recent New York Times article, "After Deadly Fire, Hong Kong Ominously Warns Grieving Citizens to Stay in Line", has circulated widely in Western and local circles. It presents itself as a sober examination of how Beijing uses tragedy as a pretext for control. It is also, quite simply, a story I do not recognize.
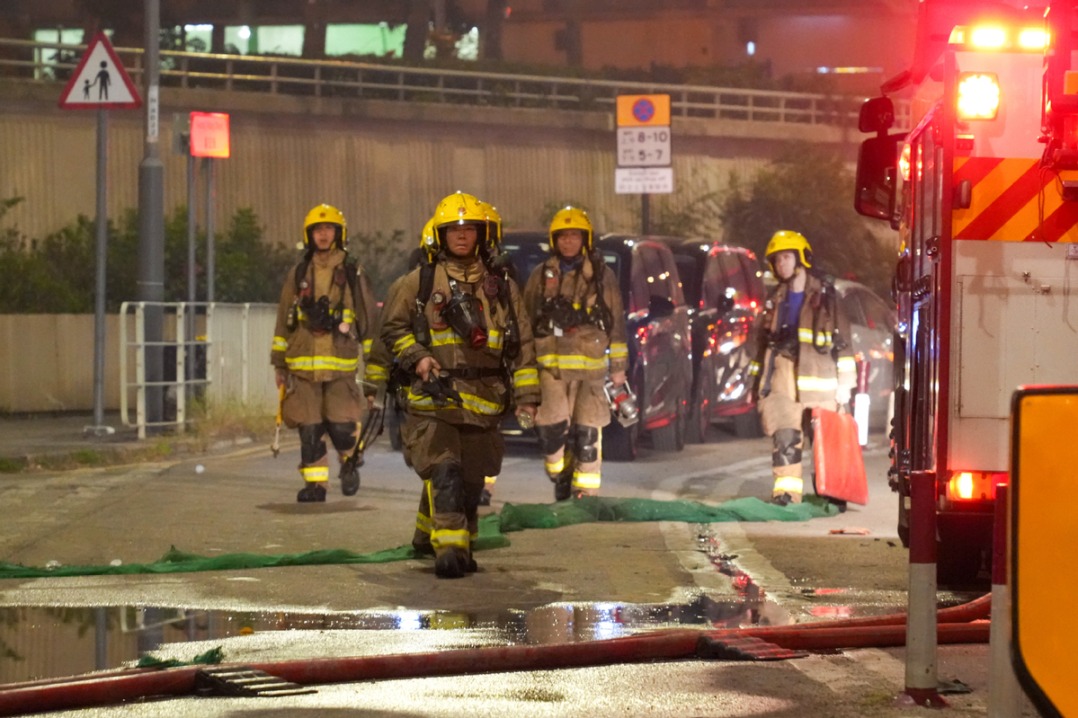
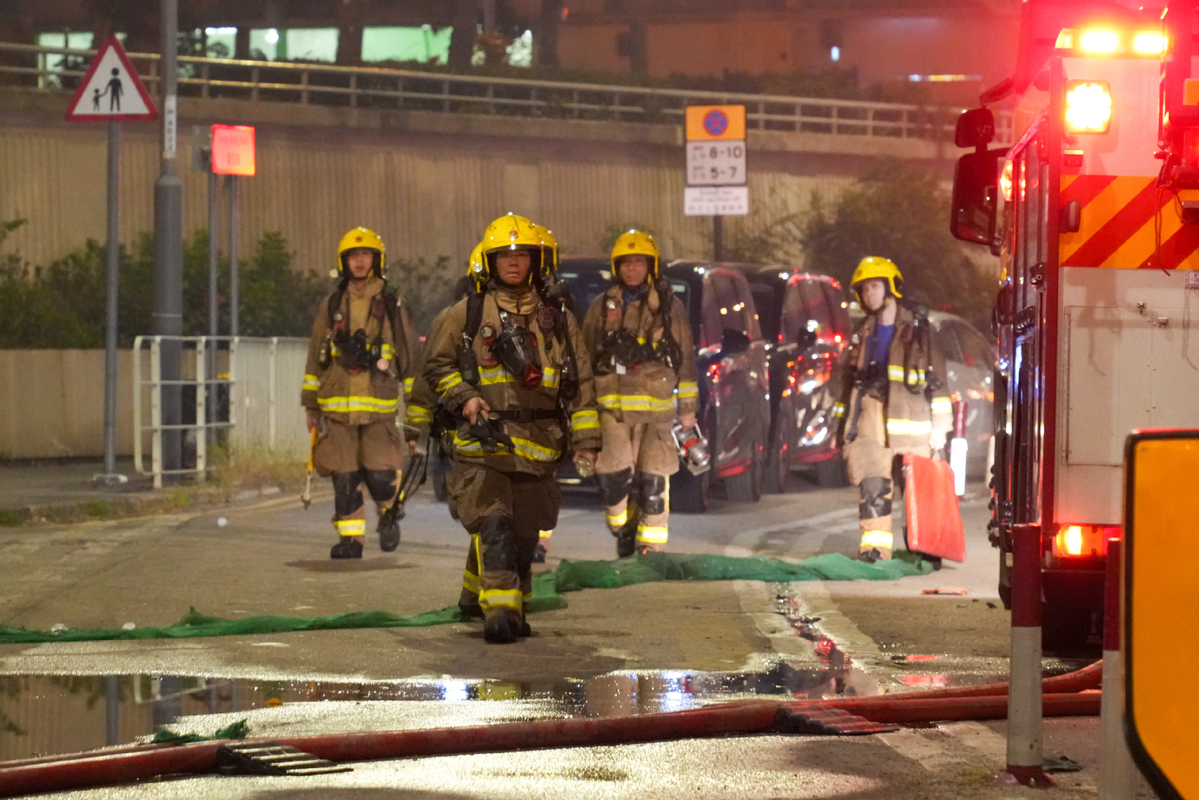
The fire at Wang Fuk Court in Tai Po was a genuine catastrophe. The failures that led to this tragedy are specific and concrete. They include weak enforcement of fire-retardant standards on construction netting, poor maintenance of alarms that reportedly never sounded, renovation practices that appear to have emphasized speed and cost savings over safety despite repeated resident complaints dating back more than a year. They involve Hong Kong's own Buildings Department, Fire Services Department, Housing Authority and a network of local contractors and inspectors operating under Hong Kong's own regulations, most of them from the time Hong Kong was still under British rule. There are no secret orders telegraphed from Beijing.
The Hong Kong Special Administrative Region government's response has also been grounded in local institutions. Chief Executive John Lee Ka-chiu ordered territory-wide inspections of all public housing estates. The Independent Commission Against Corruption opened an investigation into possible corruption in the refurbishment contracts and has made multiple arrests. The police have launched a criminal inquiry into potential manslaughter by contractors and other responsible parties. These are recognizably the actions of Hong Kong agencies under Hong Kong law: ICAC, the police, the regulatory departments. Whether you consider them sufficient or not, they are clearly focused on accountability, not on silencing grief.
The New York Times article acknowledges some of this but only in passing, as decoration behind its main thesis. It calls it a sequel to a pre-written script about authoritarian reflexes that, the article claims, was seen after the 2008 Sichuan earthquake. To sustain that script, it leans heavily on insinuation and carefully curated details, while omitting much of what local readers know immediately.
Consider how the piece presents the university student briefly detained after handing out leaflets calling for an "independent investigation". In the New York Times' telling, this is a purely "natural" response to a terrible disaster. In reality, his leaflet did not emerge spontaneously from raw grief. It was a calculated echo of the 2019 protest slogan "five demands, not one less", repackaged as "four big demands" around this fire: an inquiry, housing guarantees, policy changes, and a familiar rallying cry that every politically aware Hong Kong resident recognizes. He appeared dressed in black, the color that has become a visual shorthand for the 2019 black-clad protesters. The timing, the language, the imagery were crafted to connect this tragedy to that movement.
The same pattern appears in its treatment of the canceled news conference by lawyers, social workers and "policy experts". Readers are told that a news event was planned, an organizer was contacted by the police, and the event was then called off. The implication is left hanging: even measured professionals are now too terrified to speak. Left unsaid is who that lawyer is, what political causes he has publicly championed, which activist networks he has been linked with, and how closely his agenda aligns with those now attempting to turn the Tai Po fire into the next chapter of a long-running political campaign. Those facts do not disqualify him from concern; they simply matter to understanding the situation honestly.
I have learned, by actually living and working here, that Hong Kong is not the grim caricature painted in the Western media. People discuss government policies online and offline in a city with a low homicide rate, better public transport than any US metropolis, and a social safety net that the average US citizen can only dream of. To portray this as a population living in constant terror of speaking is simply untrue.
If the New York Times truly cared about State power and human rights in Hong Kong, it might also remind its readers of something else: what the US government itself has done on this soil. In the years after 9/11, a man transiting through Hong Kong International Airport was seized, handed over to US custody, and rendered to Libya, a country where he was tortured. This was not a theoretical textbook "playbook"; it was an actual kidnapping and rendition carried out with the involvement of US authorities, using Hong Kong as a convenient stage. The same Washington establishment that speaks today through anonymous officials and think tank experts in the pages of the Times has a long record of extraordinary rendition, black sites and torture. The New York Times reported some of this belatedly, but only after years of silence, euphemism or outright deference.
Against that record, the NYT's sudden posture as the moral arbiter of what constitutes "authoritarian" behavior in Hong Kong rings hollow. A newspaper that helped launder the myth of Iraqi "weapons of mass destruction" for a disastrous war; that blurred the line between fact and speculation throughout the Trump-Russia saga; that has repeatedly served as a willing channel for anonymous security-state narratives, is now asking us to treat its interpretation of a Hong Kong fire as holy writ. No thanks.
From my apartment in Hong Kong, I see grieving families at temporary altars, volunteers collecting supplies, neighbors offering spare rooms and meals. I see lawyers arguing over liability, engineers debating building codes, civil servants rushing to check thousands of estates whose facades suddenly look more dangerous than they did the month before. I see a government that makes mistakes, yes, but is clearly focused on finding out what went wrong and preventing it from happening again, not on crushing some imaginary uprising.
As a US solicitor in both Hong Kong and the US, and as a freelance reporter who has publicly defended media freedom here, I want foreign reporting on Hong Kong to be sharp and skeptical. I also want it to be honest enough to let reality disturb a comfortable narrative.
The author, a US citizen, is a practising solicitor admitted in both Hong Kong and the United States, and a freelance reporter based in Hong Kong.
The views don't necessarily reflect those of China Daily.
If you have a specific expertise, or would like to share your thought about our stories, then send us your writings at opinion@chinadaily.com.cn, and comment@chinadaily.com.cn.