Gene designing delivers crops with higher yields

A major research program aimed at designing seeds with greater precision has delivered tangible gains in crop yields and resource efficiency, marking significant progress in strengthening food security and sustainable agriculture, scientists said.
Launched in November 2019, the Chinese Academy of Sciences' Strategic Priority Research Program on "Precision Seed Design and Breeding" has identified a series of key genes linked to higher yields, improved quality, more efficient fertilizer use, and stronger resistance to disease and environmental stress.
Researchers have developed 37 pilot crop and aquaculture varieties designed to boost output and quality while reducing input costs and losses. These varieties have been promoted across about 965,000 hectares of farmland nationwide, said Li Jiayang, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the program's chief scientist.
The program, led by the academy and in collaboration with about 30 research institutions, focuses on major crops such as rice and wheat, as well as aquatic species. It has designed the varieties to achieve a 10 to 20 percent increase in yield, a 15 to 20 percent reduction in inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides, or a 15 to 20 percent reduction in losses.
"Over the past six years, we have uncovered key genes and regulatory networks that support high yield, quality and resilience," Li said. "This has allowed us to create new varieties that perform better while using fewer resources."
One breakthrough involved identifying a key gene that enables rice to maintain stable yields even when nitrogen fertilizer use is reduced by 20 to 30 percent.
Chong Kang, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and a researcher at its Institute of Botany, said the discovery of a gene known as TCP19, which improves nitrogen-use efficiency, gives farmers a way to cut costs and reduce pollution without sacrificing output.
In wheat, researchers focused on reducing losses caused by major diseases. New varieties have been developed to lower pesticide use and secure harvests. Zhongke 166, a high-yield, scab-resistant wheat variety developed under the program, has already been planted across nearly 100,000 hectares of farmland, Chong said.
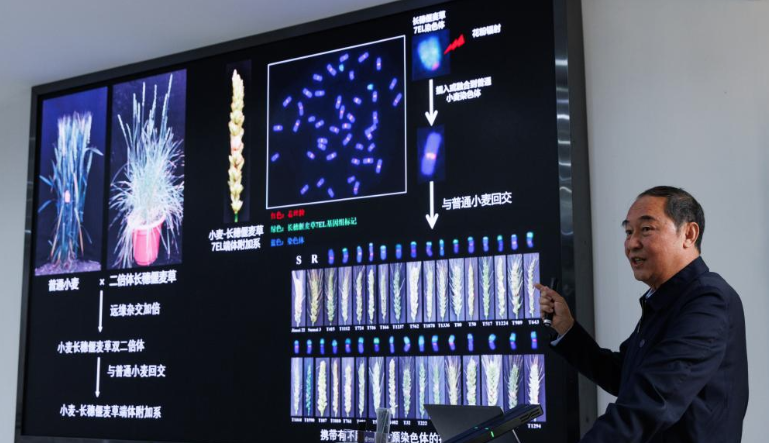
A team led by Gao Caixia at the academy's Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology developed a new genome-editing approach that overcomes the long-standing trade-off between disease resistance and high yield.
Using the technology, the researchers created a wheat variety that is both resistant to powdery mildew and high-yielding. In 2024, the breakthrough earned China's first biosafety certificate for the production and application of a genome-edited staple crop.
Scientists have also developed new strains of silver crucian carp that grow faster, survive better and convert feed more efficiently.
Gui Jianfang, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and a researcher at the academy's Institute of Hydrobiology, said one new candidate variety, Zhongke 6, grows about 25 percent faster than earlier strains.
Xue Qiang, head of the academy's Bureau of Science and Technology for Sustainable Development, said the significance of the program goes beyond maintaining backup seed resources.
"Future breeding efforts aim to produce seeds that are not only higher-yielding but also more nutritious, water-saving and resilient to climate stress," he said.
Chong said key areas for future research include understanding how multiple traits — such as yield, quality and resilience — can be combined more effectively. He added that improving crops' adaptation to climate variability and addressing challenges related to genetic transformation, regeneration and genotype dependence will also be prioritized.